Signs of a Ruptured Eardrum
Recognizing eardrum damage symptoms are a signal that you need to seek the help of a doctor of audiology or ENT doctor. Signs of a ruptured eardrum can include:
- Sudden hearing loss (deafness or muffled sound)
- Earache or ear pain (ongoing or comes and goes)
- Itching in your ear
- Fluid leaking from your ear (mucus-like, pus-filled, bloody drainage)
- Running a fever
- Ringing or buzzing in your ear (tinnitus)
- Spinning sensation (vertigo)
- Nausea or vomiting resulting from vertigo
These symptoms go away once your eardrum has healed or any infection in your ear has been treated.
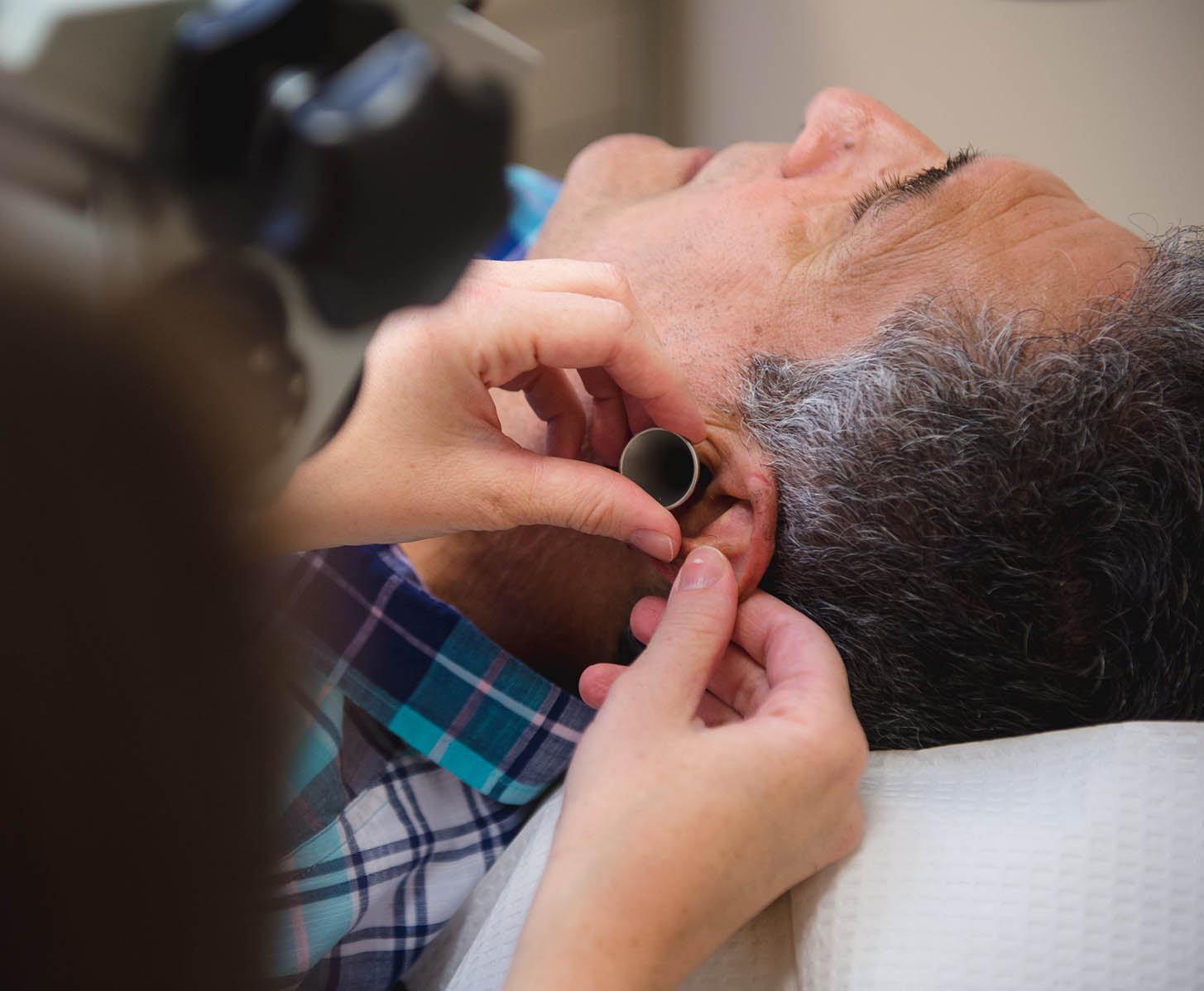
What to Expect During Your Appointment for a Perforated Eardrum
- Symptoms you are experiencing (hearing loss, fluid discharge, fever, tinnitus, dizziness, etc.)
- Any activities that might have led to a traumatic event (head trauma, foreign objects in your ear, explosions, etc.)
- Recent ear infections
- Recent air travel, swimming, diving, or rapid changes in pressure
- Medications, including any vitamins or supplements you’re taking
After discussing your case, your ENT specialist will conduct a visual inspection of your ear using an otoscope, which is a magnifying glass with a tapered end with a light on it.
Once testing is complete, you and your doctor will discuss the results of your evaluation and come up with the necessary treatment solutions to heal your eardrum rupture and any other challenges that might be associated with it, such as an infection or permanent hearing loss.
Perforated Eardrum Treatment
In more severe cases, interventions might include an eardrum patch, which is a synthetic patch used to close a tear or hole in the eardrum that won’t close on its own. This is an in-office procedure done by an ENT.
In the event that neither natural healing nor an eardrum patch provides the desired effect, your ENT might recommend a surgical intervention known as a tympanoplasty. A tympanoplasty is an outpatient procedure with an 85-90% success rate that involves grafting a patch of your own tissue to close the hole in the eardrum (if general anesthesia is necessary, a longer hospital stay may be required.)
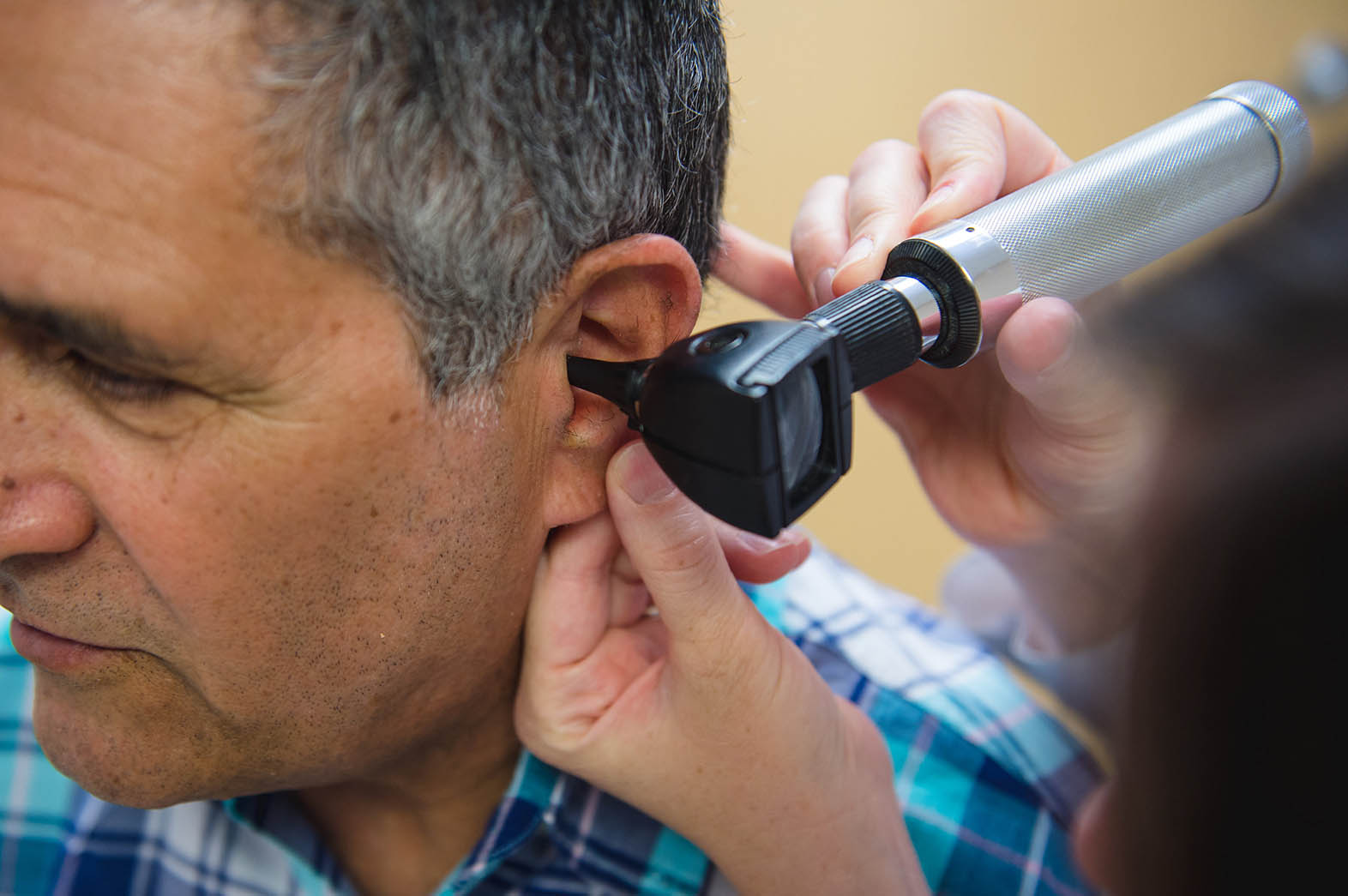
Consult Scottsdale ENT for Treatment of a Ruptured Eardrum
Most tympanic membrane perforations (TMPs) heal on their own within six weeks to three months, but you will want to seek the help of our ruptured eardrum specialists at Scottsdale ENT to treat any existing infections, ensure that your condition doesn’t lead to an infection or to repair a TMP that won’t heal on its own.
To learn more about how we treat a ruptured eardrum or to schedule a consultation, just complete and submit the adjacent form and we’ll contact you to answer your questions or schedule an appointment.
You Might Also Be Interested In
The latest news, technological breakthroughs, and patient resources available from the experts at Scottsdale Ear, Nose & Throat.

